الأمراض
الصداع النصفي \ الصداع
Are you suffering from headaches? You are not alone! Headache is a widespread disease. It occurs in different types and strengths and can impair the quality of living substantially. It is possible to do something against it. But before a therapy can be started it has to be found out what the reason is and a correct diagnosis has to be made.
There are many types of headaches. The most common are the primary headaches like migraine, tension headache or cluster headache or an analgetic headache. Your neurologist has to know how your headache feels like, where it starts; whether there are accompanying symptoms, how long it lasts and how often it occurs. Then he will do different medical examinations. After he knows the diagnosis he can give you an advice for the right treatment. Treatment is possible!
Migraine - more than only headache
Migraine is one of the most frequent neurological diseases. Around the world about 10 percent of the adults are suffering of migraine, more women than men. The difference between the genders has most likely hormonal and genetic reasons. Typically it starts in adolescence. After the 50th year the frequency declines again.
It is a temporary dysfunction of the brain. During a migraine attack the blood vessels of the cerebral membrane are widened and infected. The nerve fibres around the vessels are irritated so heavily that they send pain signals.
The duration of a pain attack is between 4 to 72 hours. The frequency varies between once a year up to twice a week. The pain is moderate up to very violent. The characteristic is mostly pulsating and only on one side of the skull; but in some patients also on both sides. One side is more affected than the other. Very often people are having accompanying symptoms like nausea, vomiting, visual problems and are very sensitive against light, noise and odour. By physical exercises the pain increases.
There are different migraine triggers like stress, menstruation, alcohol, especially red wine, disturbances in the sleep-awake-cycle, irregular meals, weather changes, light stimulus, odour or pain in the neck. These triggers are very individual and vary even in one individual from time to time. But these triggers are not the causes of the disease they just stimulate it.
A typical migraine attack proceeds in 4 phases. During the lead time there exist no pains yet. There could be depressive reactions, irritability and agitation. Concentration might get reduced; people feel tired and have to yawn a lot. Oedema, constipation or a craving for sweet or greasy food may occur. The second phase might be an aura. Quite often there are visual problems with scintillating scotomas or double vision. But it also can be sensibility disturbances or movement and speech problems. An aura keeps from a few minutes up to one hour.
The third phase is the headache phase. The pulsating pain starts very often in the neck, spreads over the back of the head and settles behind the eye or at the temple. Most attacks are accompanied by vegetative symptoms. The whole body is affected. Some people are not able to continue their work. They have to lie down. They seek quietness and darkness, don`t want to hear or see anything or anybody. The duration of the headache might be up to 3 days if the attack is not interrupted by medication.
Hours or 1-2 days after a migraine attack (4th phase) people feel tired and exhausted, concentration is still reduced, mood might be swinging.
What can you do to ameliorate the migraine? Be active, you can do something.
Migraine prevention without medication:
Reduce stress factors as much as possible.
- Learn good time management: plan your day schedule. Don`t forget enough time for brakes.
- Learn to say “No”.
- Don`t spread yourself too thin. Not everything has to be done right away.
- Think: “nobody is perfect!”
- Take life easier, enjoy it.
Relaxation: Proceedings for recreation as Yoga, autogenic training or progressive muscle relaxation techniques help, but have to be done regularly
Endurance sports like cycling, walking, jogging or swimming are good. But it is important to exercise regularly, at least three times a week for about 30 minutes.
Try to have e very constant sleep-awake cycle, also during the weekend. And eat and drink with regularity.
Avoid your personnel migraine triggers.
Migraine prevention with medication:
Migraine Medical prophylaxis
In severe cases it is useful to take special medication every day to reduce the number of attacks, the length of the single attack or to improve the effect of the acute medication. This medication has to be taken for at least three quarters of a year, sometimes longer. Your neurologist will find out which medication will be the best for you and will supervise you through the therapy.
Therapy of the acute migraine attack:
There are different types of medication to treat the acute attack. In easier cases a painkiller like Panadol or Ibuprofen can be enough. A combination with a medication against nausea can be given. But mostly stronger medication is required. The triptans, a group of special migraine drugs, ameliorates the attack within 2 hours in most patients. The medication has to be taken as soon as possible. Then it helps the best. But be careful. You should not take any painkiller or any triptan more often than 10-12 times a month. Otherwise there is the danger to develop an analgetic headache, which means headache by the medication itself!
الدوار
Vertigo Causes
The causes of vertigo may be manifold. Most often vertigo is the consequence of damages to the internal ear, the equilibrium, the cerebellum or due to circulatory disturbances of the brain. But also heart diseases or low blood pressure may cause vertigo and dizziness. Even psychic disorders like panic attacks or anxiety can lead to vertigo.
Vertigo Diagnosis
It is therefore imperative that the exact nature of all vertigo complaints is determined in a multidisciplinary way involving especially the examination by a neurologist, an ear nose and throat specialist and a cardiologist.
Vertigo Treatment
Only the correct diagnosis can lead to an effective therapy either by medication, by special physiotherapy or psychotherapy or a combination thereof.
Professor Dr. med. Detlef Koempf – Neurological Expert for Vertigo & Visual Problems

Professor Koempf, Specialist for vertigo & visual Problems, is a genuine German University Professor born in Saeckingen, near Freiburg and studied medicine in Heidelberg.
After having spent one year of research in the USA, he continued his medical education at the University Hospitals Mannheim and Heidelberg and went on to work as Deputy Head at the Neurological Hospital in Erlangen.
From 1987 until 2010, Professor Koempf held the position as Director of the Neurological University Hospital of Luebeck, Germany where he worked as a Senior Consultant for Neurology, held lectures and taught students. In 2010 he was elected as General Secretary to the EFNS (European Federation of Neurological Societies) where he organizes large neurological conventions and further education for neurologists in Eastern Countries such as Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldavia and others. Aim of these efforts is to standardize neurological diagnostics and treatment in Europe.
In 1998, Professor Koempf wrote an important book on the topic of “Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology”, vertigo and visual problems which was published by the renowned Thieme Publishers. He also deals with all “Diseases of the Cranial Nerves” on which he also published a book in 2006.
Since finishing his Univerity career, Professor Koempf has been seeing patients in his private clinic in Luebeck and spends some months in Mallorca, Spain, in a Vertigo Center which he founded at Juaneda Hospital.
During his active time as Director of the Neurological Hospital at Luebeck University, Professor Koempf dealt with the whole range of neurological diseases including Parkinson’s disease, Epilepsy, Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral circulatory disorders, stroke prophylaxis, disturbances of the memory, dementia, headaches, migraine, polyneuropathies, restles legs syndrome, back pain and diseases if the discs.
But above all, he concentrated on the numerous kinds of vertigo (of which there are about 50) as well as vision disorders or disturbances of the equilibrium. Vertigo itself is just a very general term which does not mean anything specific. One must differentiate between specific vertigo meaning everything is spinning and unspecific vertigo which may mean short loss of vision, dizziness or disturbed equilibrium.
The problem always is to find the underlying cause because very often the cause of very strong symptoms may be quite harmless whereas a slight symptomatology may indeed have a dangerous cause. In the latter case, a fast course of diagnostics is of the utmost importance in order to prevent for instance a stroke. The whole range vertigo lies between these two poles.
The most important issue when dealing with vertigo symptoms is the medical history and the correct analysis of the symptoms. At the beginning of this procedure there will be a thorough neurological examination with a focus on the eye movements. From time to time it will be necessary to carry out a psychiatric exploration as well because vertigo can be due to psychic problems. Following this will be neurophysiological investigations such as EEG, VEP, AEP or others and the DUPLEX ultrasound examination of the cranial arteries and a combined cooperation with an ENT doctor, an ophthalmologist, maybe an orthopedist and a qualified laboratory.
Despite his being in Dubai only recently, Professor Koempf realized that all services he needs for his highly specialized work are available in Dubai, predominantly offered by German colleagues such as ophthalmology, ENT, orthopedics, cardiology and laboratory. This makes diagnostics and treatment easier since they all follow the same high German standards and uncomplicated communication between them allows secured results. Professor Koempf is devoting some of his time at the moment to meeting and getting to know these colleagues in order to guarantee best results for his patients.
As main problems in this region, Professor Koempf notices so far the often faulty medicinal treatment of patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy, missing preventative measures for stroke and other diseases of the vessels as well as pain therapy regarding the numerous kinds of headaches or polyneuropathy caused by diabetes. Above all he is concerned about people suffering from dizziness and vertigo which is one of the most prevalent complaints presented in a neurological clinic and not to be underestimated regarding the possibly underlying serious causes.
Professor Koempf will continue to inform us about the topic of vertigo on this site.
آلام أسفل الظهر \ آلام العمود الفقري
In their anatomical course through the body and the limbs nerves might be damaged in various ways, the cause of damage most often being traumatic. Symptoms of nerve damage may be prickling, numbness and pain but also palsy or disorders of the bladder or the rectum. Lower back pain is one of the most common complaints today. Up to 80% of the US-Population will suffer from back pain at least ones in their lives. Back pain or lumbar pain is the largest cause of work-related absence in the United Kingdom.
Very often nerves are trapped at the spinal cord, the backbone or in their course to the limbs. The reason for this may be some injury, a slipped disk or the trapping of a nerve in a bony or connective tissue canal. A typical example is the carpal tunnel syndrome.
What to do? Prior to surgical decompression therapy, reliable neurological diagnostic methods should be applied to locate the damage exactly. Symptomatic therapy including physiotherapy and special back pain therapy might also be of help.
إضطرابات النوم
Sleep disorders are becoming a global problem these days. More and more patients come to our GNC Center in Dubai Healthcare City complaining “I can’t sleep!” “I’m always feeling tired”. Our neurologists at GNC know how to deal with these problems.
Sleep Disorder Definition
Sleep studies are of essential importance for all those (even children) suffering from sleep disorders (problems with initiating and maintaining sleep, snoring, sleeplessness, disturbed rhythm of sleep, somnambulism, etc.), since the various forms of sleep disorders may indicate some serious illness such as narcolepsy, an epilepsy related disease or respiratory failures during sleep such as sleep apnea. On the other hand, stress related or other psychiatric disturbances may cause sleep disorders or vice versa, just as inappropriate bedding.
For all these reasons it is of the utmost importance to analyze sleep and sleeping customs thoroughly in order to determine by aid of the neurologist the individually correct diagnosis and ensuing possibilities of treatment.
The sole application of sleeping drugs does not represent an ideal solution but may even be dangerous because it could lead to dependencies as unwanted side-effect.
Other methods, such as relaxation techniques or Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) will lead to sustained changes of habit and improvement of the sleep.
Close cooperation with ENT-Clinics even enables us to diagnose potentially life-threatening cases and together find the suitable kind of therapy such as CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) or oxygen application.
Sleep Disorder Diagnostics (Polysomnography )
Thanks to modern technology, Polysomnography was discovered and is considered to be a powerful tool to diagnose sleep disorders. Polysomnography is a comprehensive recording of physiological changes that occur during sleep such as brain waves, oxygen level in the blood, heart rate and breathing rate as well as eye and leg movement. It is used to diagnose or rule out many types of sleep disorders, including Narcolepsy, Restless legs movements, REM behavior, Parasomnias and sleep apnea. This procedure is often requested or ordered for patients with frequent complaints of excessive daytime fatigue .nd severe sleepiness that may be caused by interrupted sleep.
How to Prepare for the Sleep Disorder Test
There are no major preparations necessary. The patient is advised not to take any sleep medicine or drink alcohol or caffeinated beverages prior to this test.
Risk factors of the Sleep Disorder Test
Polysomnography is a non invasive procedure. There is no risk, except maybe some skin irritation caused by the adhesive used to attach the sensors to the skin. It is therefore a fabulous procedure for children too.
Mechanism of the Sleep Disorder Test
Physiologic sensor leads are placed on the patient in order to record the following:
1. EEG (Electroencephalogram)
2. EOG (Electro-Occulogram)
3. EMG (Electromyogram)
4. ECG (Electrocardiogram)
5. Airflow (thermistor or thermocouple sensor)
6. Respiratory Effort (piezo crystal effort sensor)
7. Oxygen saturation (Pulse oximeter)
Procedure of the Sleep Disorder Test
1. AT A SLEEP LABORATORY OR HOSPITAL
For the standard test, the patient comes to a sleep lab in the early evening, and over the next 1–2 hours is introduced to the setting and "wiring up" so that multiple channels of data can be recorded when he/she falls asleep. The sleep lab may be in a hospital, or in a center. A sleep technician should always be in attendance and is responsible for attaching the electrodes to the patient and monitoring the patient during the study. She must explain to the patient about the procedure to keep the patient relaxed throughout the night.
The sleep laboratory should be equipped with video cameras in the patient’s room, so that the patient can be recorded while sleeping. This allows the technician to review the tape at any time during the test and verify whether strange looking waveforms were caused by an actual arousal, a period of wake, or normal patient movements in bed.
2. AT HOME
Nowadays, neurologists may carry out home studies to enhance patient comfort and reduce expenses, which is in the best interest of any patient. The patient is given thorough instructions as to how the screening tool is used. He will then use the equipment at home in his usual sleep surroundings and return it the next day.
Most screening tools consist of an airflow measuring device (thermistor) and a blood oxygen monitoring device (pulse oximeter). They are small and easy to handle and produce excellent graphs and other results.
At the German Neuroscience Center our neurologists follow this new path and provide patients with a tool they can easily apply at home rather than putting the patient into an awkward situation at the clinic because they realize that especially in Arabic countries with prayer times and similar rules to follow, it might be difficult for the patient to carry out a sleep study outside their homes.
The patient will sleep with the screening device for at least one up to several nights, and then return the device to the neurologist.
The neurologist will retrieve data from the device and can make assumptions based on the information given, for example, a series of drastic blood oxygen desaturations during night periods may indicate some form of respiratory event (apnea). At a minimum, the equipment will monitor the oxygen saturation.
Sleep Disorder Test Summary
Polysomnography (PSG) has proved to be a convincing tool for enhancing our understanding of sleep and its disorders. It is an essential diagnostic procedure to clarify the causes of sleep disorders thus enabling the neurologist to determine an appropriate form of treatment.
Ideally, and in accordance with international guidelines, sleep studies will be carried out by neurologists in close cooperation with an ENT specialist in such cases where first results point at a serious disease, as is standard at the German Neuroscience Center GNC.
Evaluation of sleep disorders must be made more readily available to the hundreds of thousands of patients with sleep disorders who still lack diagnosis and treatment. Lack of sleep or permanently disturbed sleep will lead to reduced concentration and failing personal efficiency. This will not only gravely affect the patients’ private lives but also their daily working capacity.
Sleep disorders, if not analyzed and left untreated, may lead to dangerous, even fatal, situations and social decline by, for instance, losing one’s job. Today, thanks to Polysomnography, nobody has to take such risks, since our neurologists, psychiatrists and psychologists at the German Neuroscience Center know of many ways how to treat sleep disorders adequately after having analyzed and diagnosed the causes thoroughly.
Soraya Waradij, B.Sc.
Neurophysiologist
German Neuroscience Center, DHCC, Dubai
References:
1. Collop NA, Anderson WM, Boehlecke B, et al. Clinical guidelines for the use of unattended portable monitors in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adult patients. Portable Monitoring Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J Clin Sleep Med . 2007;3:737-747.
2. Personal communication: Michael E. Garrison RSPGT, Supervisor Sleep Disorders Center KUMC.
3. Rechtschaffen, Allan. Kales, Anthony. A Manual of Standardized Terminology, Techniques and Scoring System for Sleep Stages of Human Subjects. Brain Information Service/Brain Research Institute. UCLA Los Angeles, CA. 1986.
4. McDonough, James T. Stedman’s Concise Medical Dictionary. 2nd edition. Williams and Wilkins Publishers. Baltimore, MD. 1994.
5.Sheldon SH, Spire J-P, Levy HB. Pediatric Sleep Medicine. W.B. Saunders, Co. Philadelphia, PA. 1992.
6. G. Hayak E. Ruther, Insomnie Schalffosigkeit, 1995
الخرف و مرض الزهايمر
Dementia is a syndrome or rather generic term to describe symptoms that follow or accompany various diseases of the brain.
Restrictions of the following neuropsychological or cognitive functions are typical features of dementia:
1. memory
2. orientation
3. comprehension and speech faculty
4. the ability to write and calculateAlzheimer’s disease
(The most common form of dementia)
In the case of Alzheimer’s disease certain proteins accumulate inside or outside of the nerve cells of the brain. The thus affected cells deteriorate. This is why Alzheimer’s disease is called a neurodegenerative disease. The degenerated cells can no longer carry out their usual function and the distribution of neurotransmitters is reduced rapidly. The consequence of this is dementia.
Although this kind of dementia is not curable as yet, the progress of dementia may be slowed down by modern medication and mental training.
Apart from these fairly common forms of dementia there is a large variety of illnesses accompanied by dementia.
In any case, the first signs of dementia should be examined closely at an early stage to gain a secured diagnosis and act accordingly.More information about dementia
Vascular dementia
(Second most common form of dementia)
Vascular dementia is caused by a vascular disease of the brain. Microangiopathies (damages to the small vessels) or macroangiopathies (damages to the large vessels) for example by arteriosclerosis may lead to reduced local blood flow in certain parts of the brain.
The thus affected nerve cells deteriorate and can no longer exercise their task of distributing neurotransmitters. The consequence is dementia.Since this process is locally restricted, it is important to examine the exact nature of dementia in order to start effective therapy at an early stage.
السكتة الدماغية
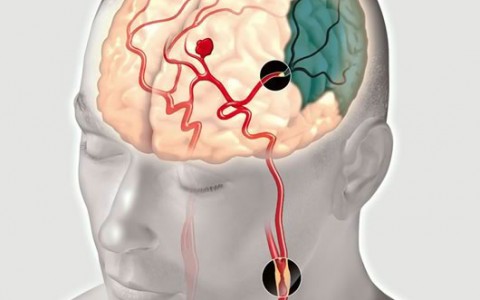
A Stroke is a serious illness which can be fatal. It is caused by the occlusion of a blood vessel that supplies the brain. This will lead to the disturbance of relevant physical functions such as:
Acute palsies of arms, legs or parts of the face, numbness, prickling, speech disorders as well as other neurological defects.
Another cause for a stroke can be a cerebral haemorrhage which might occur due to the bursting of a cerebral vessel. Both forms of cerebral apoplexy need immediate treatment in a specialized hospital (stroke unit) where the trained doctors will try to dissolve the occlusion or stop the haemorrhage respectively.Prior to all apopleptic events attention should be given to the above mentioned symptoms which are strong indicators of an arteriosclerotic process even though they might be only temporary. Such temporary attacks are known as TRANSIENT ISCHAEMIC ATTACKS. They must be taken seriously and must lead to the immediate consultation of a neurologist in order to avoid a more severe development of the symptoms.
After a stroke has taken place without early efficient clinical treatment and with following severe damages and disabilities, professional rehabilitation is necessary as early as possible to regain mental and physical abilities that might have been lost.
الصرع ، النوبات ، التشنجات
Epilepsy is an illness of the brain which expresses itself in fits or seizures or convulsions. The most well-known form of fit is the generalized tonic-clonic seizure or convulsions, which comes along with loss of consciousness, drop or convulsions. There are, however, other forms of seizures that are not so commonly known, which express themselves in the twitching of an arm or a leg or disorder of consciousness or absences.
The causes for epilepsy are manifold and can have their origin in brain damage or hereditary facts. However, due to the drug development of recent years there are very efficient possibilities to treat patients with epilepsy so effectively that the majority can lead an entirely normal life without any seizures at all. In severe cases neurosurgical interference may offer help.
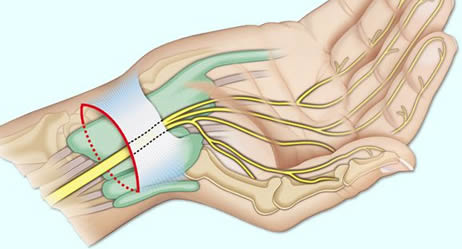
متلازمة النفق الرسغي
You've been plagued by numbness and tingling in your fingers and wrist. You are waking up at night with a "pins and needles" sensation in one hand? There might be other explanations, but the symptoms suggest you may have carpal tunnel syndrome. Is it dangerous? No. But to ignore the symptoms may cause damage of the nerve and the muscles. What is to do?In carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), one of the nerves to the hand (the median nerve) becomes compressed as it passes through the wrist. There are different causes which can lead to CTS like occupational overstressing of the hands, injuries at the wrist with malposition of the carpal bones, arthritis, pregnancy, diabetes, overweight and others. Also a genetic predisposition is discussed. In many cases, no single cause can be identified. It may be that a combination of risk factors contributes to the development of the condition.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms
The typical symptoms are numbness or tingling in the thumb, index, middle and ring finger, later pricking and painful paraesthesias. Sometimes the whole arm up to the shoulder is affected. This happens during the night or after awaking in the morning; but also with certain hand positions like keyboard typing, holding a phone or reading a newspaper, cycling or motor biking. The symptoms are intensified by overloading the hands by repetitive manual work. At the beginning the discomfort can be reduced by “shaking” the hands. Later a persistent numbness may occur. Left untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to constant pain and to permanent nerve and muscle damage that could severely limit your ability to use your hands.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnostics
If you have persistent signs and symptoms, especially if they interfere with your normal activities and sleep patterns, you should see your neurologist.
Your doctor will conduct a neurological examination. Tests with pressure on the median nerve at the wrist, produced by bending the wrist (Phalen`s maneuver) or tapping on the nerve (Tinel`s sign) can bring on the symptoms in many people. Important is to prove the feeling in your fingers and the strength of the muscles in your hand. Nerve conduction studies (an electrodiagnostic test) can pinpoint damage to the median nerve by measuring how fast electrical impulses move through it. Up to 10 percent of people with carpal tunnel syndrome, however, test is normal when this method is used. Other examinations like electromyogramm, SEPs (sensory evoked potentials), ultra sonic or MRI might be necessary to rule out other conditions like nerve root irritation or compression at the cervical spine.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment
Fortunately, for most people who develop carpal tunnel syndrome, proper treatment usually can relieve the tingling and numbness and restore wrist and hand function, especially if you catch the condition early.
Nonsurgical therapy is possible if you have mild to moderate symptoms and the neurological examinations do not show an extensive damage at the median nerve. Medication with anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Ibuprofen may help relieve pain from carpal tunnel syndrome only in the short term.
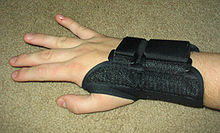
- wrist splint
The most effective conservative treatment is nocturnal splinting with a specially wrist splint. If you use it, avoid wearing it all day, since that can weaken your muscles in your wrists and hands. Wearing it all night, however, is recommended. This should be done at least for 3 month.
If the symptoms persist or the nerve conduction velocity becomes worse, surgery has to be considered. Two main types of surgery are used to relieve the pressure on the nerves inside the carpal tunnel: open carpal tunnel release and the newer endoscopic carpal tunnel release. Both are outpatient procedures performed under local anesthesia (the surgeon cuts the ligament along the middle of the palm and inner wrist). Most people make a full recovery, but in some cases (fewer than 5 percent) carpal tunnel syndrome recurs after surgery. This happens more commonly following the endoscopic procedure, which often doesn't open up the tunnel as fully as open release.
التصلب المتعدد
Multiple sclerosis is an auto-immune disease in which the auto-immune system of the body attacks the nerves and especially their myelin sheaths. The illness usually starts at a fairly young age and becomes chronic. Although this disease can as yet not be entirely cured, there is a variety of new drugs which are very effective.
Besides the necessity to apply the appropriate medication in order to alleviate symptoms like palsies, pains, vision disorders, blindness and other neurological symptoms, there are also physiotherapy and other therapeutic measures that can be helpful.
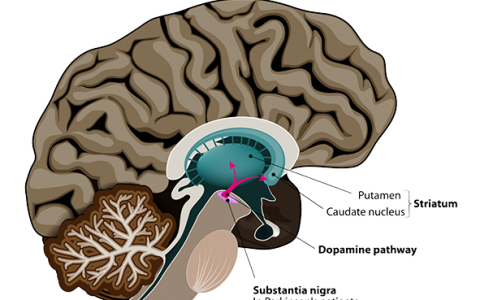
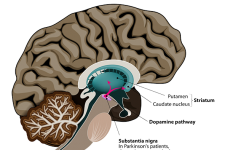
مرض باركنسون
Parkinson’s disease belongs to the group of movement disorders and expresses itself by trembling (tremor), rigidity (limb stiffness) and akinesia (diminishment of movements). Very often the changes in movement are very discreet and therefore an early diagnosis is often difficult. In the long run, however, Parkinson’s disease may result in severe handicaps and disabilities.
Aetiologically this is caused by the deterioration of specialized nerve cells which are responsible for the design, the development and the realization of movements.
However, there may be other symptoms such as a reduction of superior intellectual brain functions, psychic symptoms such as depression but also disorders of vegetative bodily functions.
Whereas in treating Parkinson’s disease the main focus will be on adequate medication, physiotherapy, dancing or other physical exercises are also useful therapeutic means.In severe cases neurosurgical intervention might be necessary which is known as deep-brain-stimulation.الاعتلال العصبي السكري
Polyneuropathy means the affection of many nerves due to very different reasons and it can therefore develop many different symptoms. Most frequent are paraesthesia such as prickling, numbness, burning of the feet, but also palsies, disorders of speech and failure of cerebral nerves.
Similar to the variety of symptoms there is also a large variety of causes for this disease. The most frequent reason is a metabolic disorder such as diabetes mellitus. But also hereditary disposition, toxic inhibition or paraneoplastic development can cause polyneuropathy.
Accordingly, diagnostics and therapy of polyneuropathies are manifold and difficult. The therapeutic aim must be to prevent the deterioration of the nerves itself on the one hand and to treat the illnesses causing polyneuropathy on the other hand.
Should both turn out to be impossible, palliative methods may be used to ease the symptoms, especially pain, by applying special medication and physiotherapy.متلازمة تململ الساقين
Do you feel a creeping, throbbing, pulling, itching or needles and pins in your legs while sitting or lying? Are these symptoms overwhelming and you feel an irresistible urge to move to stop the sensations? If yes, you may are suffering from Restless Legs Syndrome.Restless Legs Syndrome Symptoms
Restless Legs Syndrome is a condition in which your legs feel extremely uncomfortable typically beginning at night when you try to sleep. The symptoms are most commonly located in the deep of the calves, in the feet and thighs, but also can affect arms. Initially the patient often get an exaggerated sense of positional awareness of the affected leg, later the sensations appear or intensify even while sitting. Movement of the affected part of the body, for instance walking around brings an immediate relief, although temporary and partial and the sensations immediately return after the movement stops. These symptoms often lead to a severe sleep deficiency with secondary tiredness and loss of concentration in job or while driving a car. Some people with severe RLS are not even able to go to work.Restless Legs Syndrome Etiology
RLS affects estimated 7 to 10 % of the young to middle aged people and 10 to 20 % in those older than 60 years. In the Middle East region approximately 3% of the general population is affected. It is twice as often in women as in men.Restless Legs Syndrome Typs
We have to differentiate between two kinds of RLS: the primary and the secondary RLS Syndrome. The primary - idiopathic- RLS is a neurological disease with unknown causes. A disturbance of the dopaminerg system is suspected. 60 % of the symptoms that occurs among family members are triggered by genetic genesis. Medication which interferes with the dopamine system helps reliably. The secondary - symptomatic - RLS is most commonly associated with iron deficiency, venous disorders, polyneuropathy ,folacit deficit, Diabetes ,renal diseases or pregnancy. 25 % of pregnant women develop a RLS syndrome in the last 3 months of their pregnancy.RLS can also be induced by antiemetic and anti depressive and antipsychotic drugs. A primary RLS should not be considered till possible medical conditions are ruled out, especially venous disorders and polyneuropathy.Restless Legs Syndrome Treatment
Patients suffering from these symptoms should go for medical advice including a neurological examination and electrophysiology to exclude a polyneuropathy. When symptomatic geneses are excluded the neurologist will find the adequate treatment. Dr. Jutta Marquardt
Dr. Jutta MarquardtSpecialist Neurology
view full articleالوهن العضلي
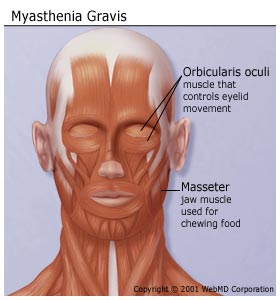
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness. The body is producing antibodies which are attacking the junction between nerve and muscle.
Most common symptoms of Myasthenia gravis are ocular symptoms (50%) of Drooping of the eyelids (ptosis), double vision (diplopia) and blurred vision. The disease can generalize including symptoms like weakness of facial and extremity muscles. Moreover patients could have difficulties in chewing, swallowing and speech. Respiratory weakness may produce acute respiratory failure.
The symptoms of Myasthenia gravis are negatively influenced by exercise, heat, illness, and stress. Normally they worsen in the evening and get better after resting.
Often myasthenia gravis is associated with other disease like rheumatoid arthritis , scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus. 65% of patients with myasthenia gravis have a hyperplasia of the thymus. 15% of patients with myasthenia gravis present a Thymoma.
Myasthenia gravis is a clinical diagnosis by specialized neurologist, supported by specific tests including Cholinesterase inhibitor tests, antibody detection test, EMG (Electromyography), Computed tomography (CT) and MRI of the chest, to detect thymoma or thymic hyperplasia.
The treatment of Myasthenia gravis is effective and most patients are able to live normal lives. Based on the clinical findings it could include certain drugs (Cholinesterase inhibitors, Immunosuppressant agents, Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG)), Plasmapheresis, Thymectomy, Physical therapy and Lifestyle changes.
الإكتئاب
Depression is a mental disease which may express itself by
1. subdued spirit
2. loss of interest
3. social retreat
4. feeling of guilt
5. reduced self-esteem
6. attention deficit disorders
7. sleeping disordersbut also by bodily symptoms like pain or paraesthesia. Depression shows various clinical pictures which makes it very difficult to come to quick conclusions. Whereas in former times depression was simply considered to be ill humour, over the last decades depression has become recognized as a very common and serious illness.
اضطراب القلق ، الإضطراب الرهابي ، نوبات الذعر
Fear is a feeling that everybody knows as being an entirely normal feeling. Fear usually is a reaction to a frightening situation such as a bank robbery or any other dangerous situation.
Normal fear turns into anxiety disorders or phobia when a fearful reaction occurs that does not correspond to the actual event, i.e. a situation that the majority of people would rate as not frightening at all, or if the anxiety reaction is so abnormally strong that the patient has the impression he is going to vomit, to faint, to die or to go insane.
اضطرابات الأكل
Eating disorders are conditions defined by abnormal eating habits that may involve either insufficient or excessive food intake to the detriment of an individual's physical and mental health. Bulimia nervosa and anorexia nervosa are the most common specific forms of eating disorders. Other types of eating disorders include and OSFED. Bulimia nervosa is a disorder characterized by binge eating and purging. Purging can include self-induced vomiting, over-exercising, and the usage of diuretics, enemas, and laxatives. Anorexia nervosa is characterized by extreme food restriction to the point of self-starvation and excessive weight loss
إنفصام الشخصية
The prevalence of schizophrenia is 0.7%. However, of the 24,000,000 sick people worldwide only about 50% are treated adequately. The majority of the maltreated patients live in developing nations. There are two kinds of symptoms – early symptoms which may exist years before the actual outbreak of schizophrenia – and main symptoms.
About 70% of the patients show early symptoms like alteration of experience and conspicuousness in conduct although to a small extent that it will not easily be brought into connection with early signs of schizophrenia.
إضطراب ما بعد الصدمات
PTSD - Post Traumatic Stress Disorder may remain for as long as six months after a traumatic event and may be prolonged for years. Typical criteria are:
- The recollection and reliving of the event, also in dreams.
- Avoidance of anything that might call back the event. This may lead to total social withdrawal.
- The feeling of mental numbness. Affects will diminish.
- Amnesia.
- General arousal, irritability, disturbance of concentration, anxious alertness, scariness, sleeping disorders.
PTSD - Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
ردود الفعل الحادة للإجهاد
Extreme life events may produce individual patterns of reaction. Such events might be the death of a partner, war, experiences, separation, accidents, experience of violence, traumata or abuse. To some people this might be the case even with simple things like attendance of school, a move or likewise. Of course it is only natural for a person confronted with a stressful event to feel sad, shocked or unable to understand what is happening.
However, if this reaction takes too long or does not stop at all or the reaction in itself is inadequate to the event thus leading to an increased impairment of the person concerned, this person needs professional help.
The reactions to life events can be manifold producing for instance restricted consciousness, decreased attention, disorientation, amnesia or depression, desperation, anxiety or aggression but also bodily symptoms like sweating, heart throbbing and blushing are common.If the reaction occurs immediately after the event and disappears fairly rapidly, this is called acute reaction to stress. This is a normal reaction. However, depending on the severity of the symptoms professional help may be needed for a short time.
الإضطراب الجسدي النفسي
It happens every so often that patients complaining about bodily symptoms consult numerous doctors and specialists without getting a sufficient explanation for their problems nor remedies. Such patients are definitely ill, they will have pains, functional disorders or likewise and yet the highly developed modern medicine seems unable to help them.
Trying to find release, such patients will consult doctors at frequent intervals which is called “doctor hopping”. Or, after years of looking for medical professional help without any result, they will turn to alternative medicine. This kind of behaviour expresses the enormous pressure these patients are under.
The problem, however, lies in the logical deduction that in case of physical symptoms or pain the solution must be bodily. If one is suffering from diarrhoea or pain in the feet, of course the obvious choice would be a specialist for diarrhoea or pain in the feet.الاضطراب الفصامى (التحويل)
Traumatic events or seemingly unsolvable problems can lead to a psychic reaction known as conversion. The unsolvable problem is deferred resulting in disturbances which the person concerned can no longer trace back to the basic event.
The problem may be deferred to the following scopes:
- Psyche: this path may lead to amnesia, flight (fugue), stupor, trance, obsession, loss of identity
- Motor system: may lead to weakness, palsy, dystonia, disturbances in coordination and loss of hold
- Sensibility: may lead to paraesthesia, prickling and physical numbness
- Brain: may lead to epileptic-like fits